OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
OFDM = Orthogonal FDM = Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
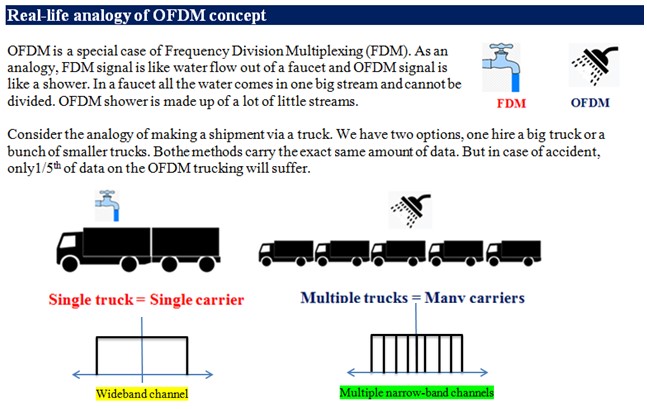
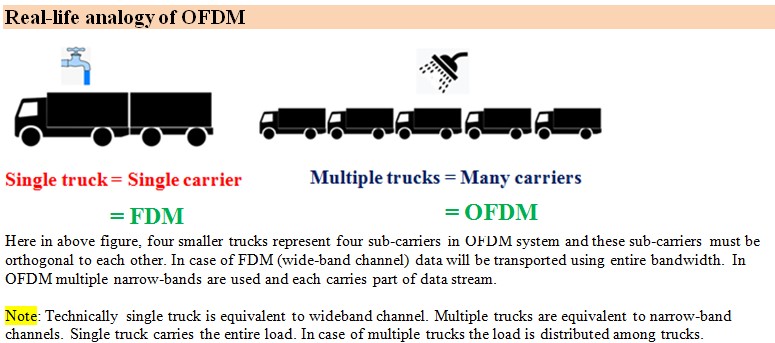
Modulation is fundamental requirement in any communication system. Multi means two or more. Multiplexing is used to transmit two or more data signals over single communication channel
OFDM is a combination of modulation and multiplexing. Multiplexing generally refers to independent signals produced by different sources.
OFDM is a combination of modulation and multiplexing. Multiplexing generally refers to independent signals produced by different sources.
OFDM = Multi-carrier communication = multi-carrier modulation technique
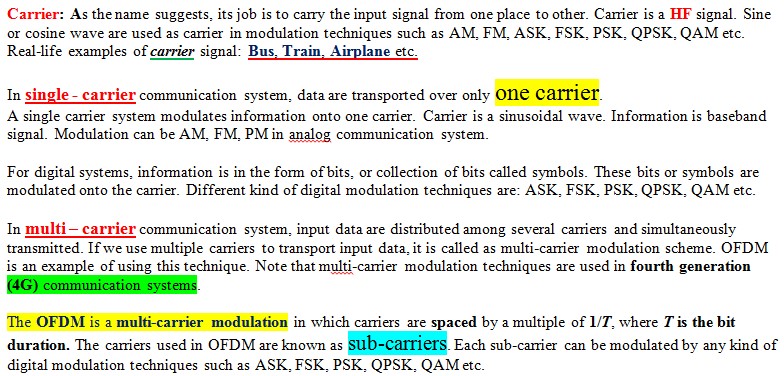
The channel is split into number of sub-channels. The important property here is any two sub-channels are orthogonal to each other. Now each sub-channel transmits a part of the original information. Every channel gives some bandwidth. So this available bandwidth is divided into N sub-bandwidth, representing N sub-carriers.
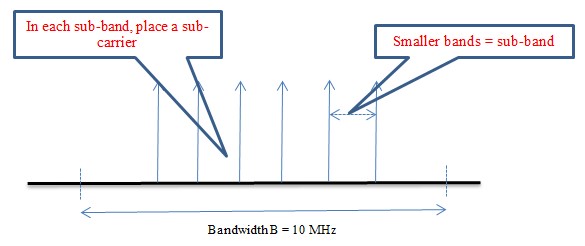
Let B = Bandwidth of channel = 10 MHz
N = Number of sub-carriers or sub-bands = 1000
Bandwidth of each channel = B/N = 10 MHz/1000 = 10 KHz
Such a system with multiple sub-bands and multiple subcarriers is termed as Multi Carrier Modulated (MCM) system. This is basis or precursor for OFDM. This enables smooth transmission and reception in a broadband wireless communication system.
The basic principle of OFDM is to split a high-rate data stream into a number of lower rate streams that are transmitted at a time over number of sub-carriers. So, OFDM converts high speed data bits into parallel low speed data flows. As a consequence of having many sub-channels, OFDM eliminates the problem of fading that occurs in multi-path propagation of radio signals.
OFDM uses large number of closely spaced orthogonal sub-carriers. Each carrier is modulated with a conventional modulation scheme such as QAM.
OFDM Basic principle
- Split high symbol rate data stream into N lower rate streams
- Transmit N lower rate data streams using N sub-carriers
- N sub-carriers must be mutually orthogonal. Any sub-carrier must be orthogonal to all other sub-carriers.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), is a form of multicarrier transmission, in which a high-rate data stream is transmitted in a parallel manner over a number of low-rate orthogonal subcarriers. By using multicarrier modulation, bits are overlayed on many carriers at the same time.