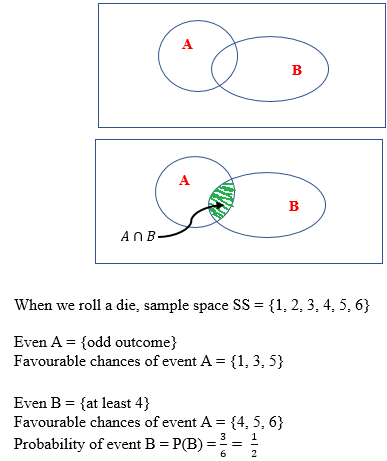
Conditional Probability | Joint Probability
Conditional probability
If A and B are two events in a sample space S, the conditional probability of A given B is defined as:
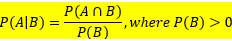
P(A|B) = Probability of occurrence of event A after the occurrence of event B
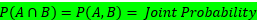
Conditional probability is defined when two events depend upon each other. Conditional probability assumes that one event has taken place and then asks for probability of other.
Value of a probability can change, if we get additional information. For example, probability of contracting lung cancer is higher among smokers than non-smokers. Here smoking is additional information.
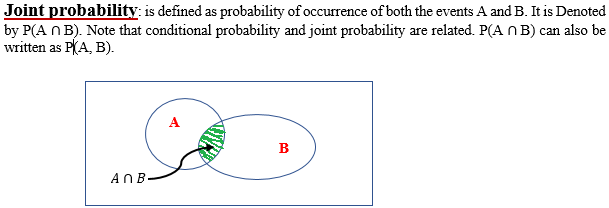
Conditional probabilities make it easier to compute probabilities of intersections. Note that conditional probability and joint probability are related.
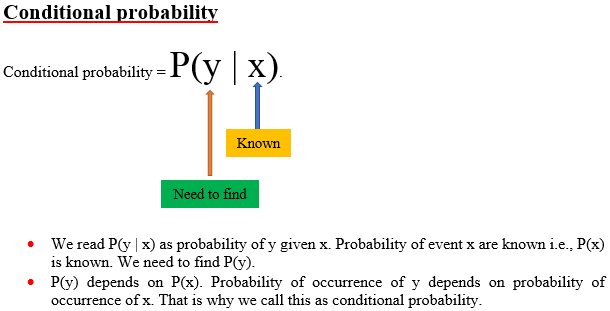
Suppose y is any given event. Now we can find P(y). In case of P(y|x) also we are finding P(y) only. But here, resultant probability depends on P(x) also. The event x is additional information on which event y depends. So, x and y events are dependent events. Note that P(y|x) is not same as P(x|y).