Frequency Shift Keying | FSK
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)
Computer data is binary in nature and consists of sequence of 1s and 0s. Telephone lines are analog in nature and can carry only analog electrical signals. So devices called MODEMs are needed to transmit data over telephone lines.
FSK is also known as 2-level FSK, because number of frequency changes = 2.
Other name: BFSK (Binary Frequency Shift Keying)
FSK modulation waveforms are shown below:
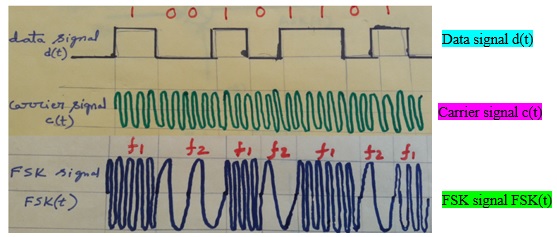

FSK rule:
- Bit 1 is represented by high frequency (f1) carrier signal
- Bit 0 is represented by low frequency (f2) carrier signal
No matter if bit 0 is represented by low frequency signal and vice versa.
FSK features are as follows:
- Number of frequency changes = Number of frequency used = 2
- Constant variables: Amplitude and Phase of the carrier
- Changing variable: Frequency of carrier
- Number of bits transmitted at a time = 1
NOTE: If the incoming bit from computer is 1, then high frequency signal (say f1) is transmitted. If the incoming bit from computer is 0, then low frequency signal (say f2) is transmitted.
NOTE: In FSK, modulating voltage (i.e., input voltage) is used to vary frequency of the carrier (Refer my video lecture on Modulation in Electronic Communication System)
