Amplitude Shift Keying | ASK
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)
ASK is also known as 2-level ASK, because number of amplitude changes = 2. Other names are: OOK (On – Off Keying), BASK (Binary Amplitude Shift Keying). ASK modulation waveforms are shown below:

As the name suggests, in ASK the amplitude of the carrier is changed according to data signal d(t). Note that d(t) is an input data signal.
ASK rule:
- Bit 1 is represented by high amplitude
- Bit 0 is represented by low amplitude
ASK features are as follows:
- Number of amplitude changes = Number of amplitudes used = 2
- Constant variables: Frequency and Phase of the carrier
- Changing variable: Amplitude of carrier
- Number of bits transmitted at a time = 1
NOTE: If the incoming bit from computer is 1, then high amplitude (say 5V) is
transmitted. If the incoming bit from computer is 0, then low amplitude (say 0V) is transmitted.
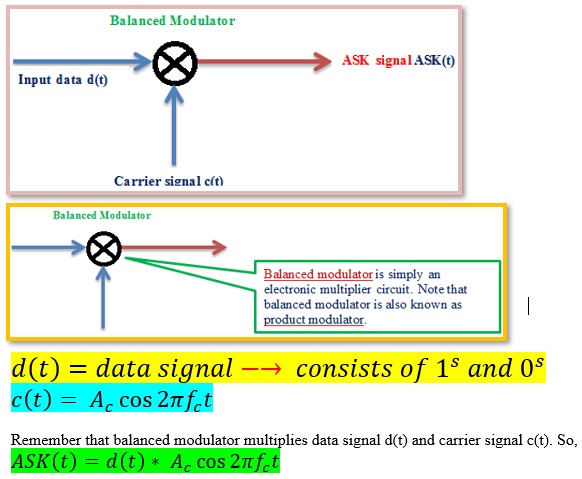
ASK Modulator: ASK modulation using balanced modulator is shown below. Remember that modulation is the process of adding carrier to the information signal.
ASK Demodulator
Note that demodulator is also known as detector. Remember that demodulation is the process of removing carrier from modulated signal. Demodulator is used to estimate the received signal. If bit 1 is transmitted, 1 should be received. If 0 is transmitted, 0 should be received. Otherwise there is no meaning of communication.
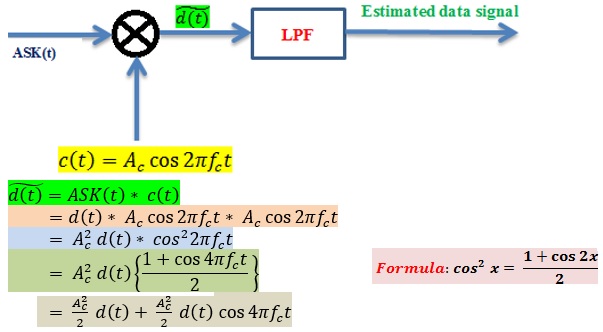
Now this signal is passed through LPF (Low Pass Filter) with cut-off frequency fc.
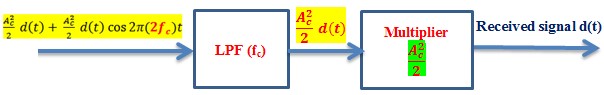
LPF passes all frequency components below cut-off frequency fc and removes all frequency components above fc. So, . Because, and the frequency of this signal is 2fc.
NOTE: ASK is very sensitive to noise and has limited application in data transmission (low bit rates up to 100 bps). Remember that changing amplitude of carrier is dangerous as amplitude changes are very susceptible to noise. That means noise easily attacks information signal.
NOTE: In ASK, modulating voltage (i.e., input voltage) is used to vary amplitude of the carrier (Refer my video lecture on Modulation in Electronic Communication Systems)