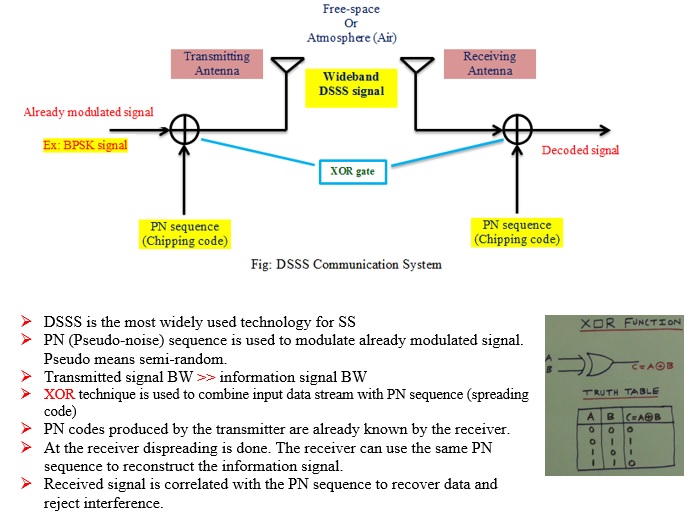
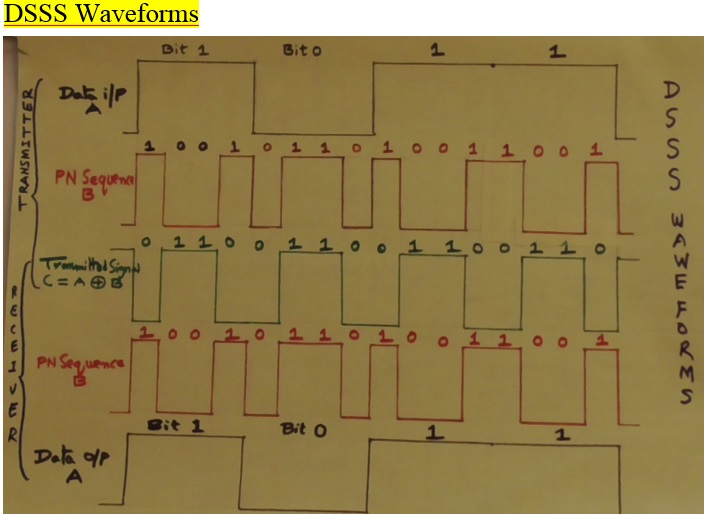
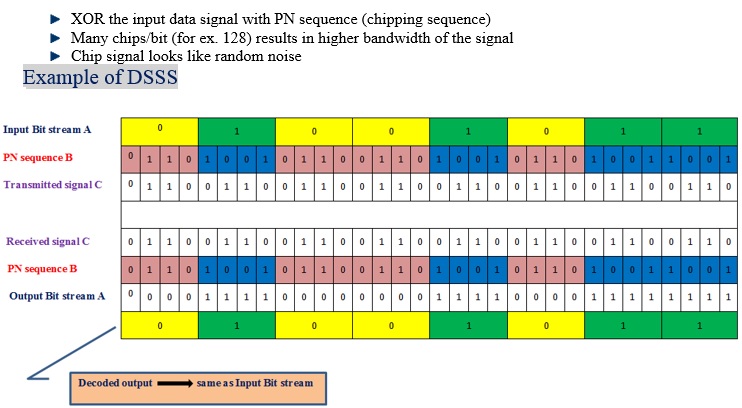
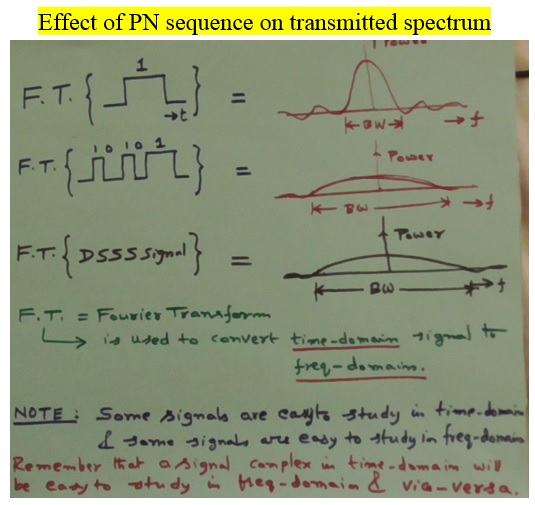
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum | DSSS
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Radio communication suffers from following problems:
- Interference
- Jamming
- Multipath propagation & fading
- Secure communication
INTERFERENCE: Real life example of interference is: two people talking at the same time. Interference may be intentional or unintentional.
JAMMING: The goal of jammer is to disturb the communication of his adversary (enemy). The jammer has a priori knowledge of most system parameters (ex: frequency bands).
MULTIPATH DISPTORTION: In wireless communication systems, there exists multipath propagation. Multipath means, there is more than one path from transmitter to receiver. Such multipath may be due to reflections from ground, buildings or other objects like trees etc.
FADING: Multipath may result in fluctuations in the received signal amplitude. This variation of signal level due to multipath propagation is known as FADING.
SECURE COMMUNICATION: Ordinary radio transmissions are easy to intercept by unwanted listeners

DSSS Applications
- Military communications
- Cordless phones
- Digital cellular telephony
- GPS satellite navigation systems
- WLAN (IEEE 802.11a, IEEE802.11b, IEEE 802.11g)
- Bluetooth
Disadvantages
- Increased bandwidth (frequency usage, wideband reciver)
- Need for good PN sequence generator and hence complex circuitry