Unguided Transmission Media
Unguided transmission
unguided transmission media do not use any physical connection between source and destination. They use air or free-space as medium. Types of unguided transmission are as follows:
- Radio waves
- Micro waves
- Infrared waves
- Satellite
Information is transmitted by sending electromagnetic (EM) waves through atmosphere (free space) and hence the name unguided media. All unguided transmission is classified as wireless transmission. A device called antenna is used to transmit and receive EM signals. Some of the types of wireless media are:
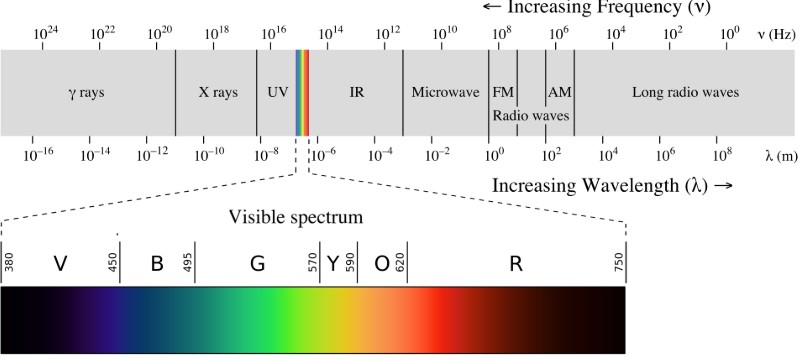
Electromagnetic waves ranging from 3 kHz to 1 GHz are called radio waves. Radio waves are used for multicast communications, such as AM radio, FM radio and television.
Radio Frequency (RF) Spectrum
| S.No. | Frequency band Name | Frequency Range (Hz) | Wave length | Applications |
| 1 | ELF (Extremely Low Frequencies) | 30 – 300 | 104 km to 103km | Power applications |
| 2 | VF (Voice Frequencies) | 300 – 3K | 103km to 100 km | Audio applications |
| 3 | VLF (Very Low Frequencies) | 3K – 30 K | 100 km – 10 km | Submarine communications, Navy and Military communications |
| 4 | LF (Low Frequencies) | 30K – 300K | 10km – 1 km (Long waves) | Marine and Aeronautical communications |
| 5 | MF (Medium Frequencies) | 300K – 3M | 1km to 100 m (Medium waves) | AM broadcast, Marine and Aeronautical communications |
| 6 | HF (High Frequencies) | 3M – 30M | 100m to 10m (short waves) | Amateur and CB communication |
| 7 | VHF (Very High Frequencies) | 30M – 300M | 10m to 1m | FM and TV broadcasting |
| 8 | UHF (Ultra High Frequencies) | 300M – 3G | 1m to 10cm (Microwaves) | Cellular phones
UHF TV channels |
| 9 | SHF (Super High Frequencies) | 3G – 30G | 10-1m to 10-2m | Satellite communications & RADAR |
| 10 | EHF (Extremly High Frequencies) | 30G-300G | 10-2m to 10-3m | Satellite communications & RADAR |
1K = 1 Kilo = 103 1M = 1 Mega = 106 1G = 1 Giga = 109 1T = 1 Tera = 1012
MICROWAVES
Frequencies > 1 GHz is known as microwaves. Microwave signals are used to transmit data without the use of cables similar to that of radio and TV signals but at different frequency range. It is line of sight transmission, which means signal travels in a straight line.
The transmitter and receiver of a microwave system should be in line-of-sight because the radio signal cannot bend. With microwave very long-distance transmission is not possible. In order to overcome the problems of line of sight and power amplification of weak signal, repeaters are used at intervals of 25 to 30 kilometres between the transmitting and receiving end.
- EM waves ranging from 1GHz to 300 GHz are known as microwaves.
- Microwaves are used for communication such as cellular telephones, satellite networks, and wireless LANs.
- Microwaves travels in straight lines
- Repeaters are necessary for long distance communications
- Microwaves can’t penetrate through buildings
- Best example is Bluetooth technology

INFRARED
Infrared transmission uses infrared light to send information. Various applications are: TV remotes, automotive garage doors, wireless speakers etc. all make use of infrared as transmission media. Infrared light transmits messages through the air and can propagate throughout a room, but will not penetrate walls.
- Infrared signals can be used for short range communication in a closed area (within room).
- Infrared signals typically used for short distances (within room). Microwave signals commonly used for longer distances (10’s of km).
SATELLITE
A communication satellite is a microwave relay station placed in outer space (36000 km above earth).
In satellite communication, microwave signal is transmitted from a transmitter on earth to the satellite at space. The satellite amplifies the weak signal and transmits it back to the receiver. The main advantage of satellite communication is that it is a single microwave relay station visible from any point of a very large area.
The most popular frequency band is referred to as 4/6 band.
Satellite is 36,000 km above the earth. So, point-to-point communication on the earth will be at 72,000 km. Hence there exists a round trip delay of 270 msec in satellite communication. This poses a number of problems.
Another interesting property of satellite communication is its broadcast capability. All stations under the downward beam can receive the transmission.
Now-a-days communication satellites are not only used to handle telephone, telex and television traffic over long distances, but are used to support various internet based services such as e-mail, FTP, World Wide Web (WWW), etc.

Satellite Features
- It appears stationary from the earth as it rotates with same speed of earth.
- Capable of receiving, relaying of voice, data and TV signals
- Weather conditions such as clouds, rain, lightning etc., may adversely affect communication.
- Satellites can provide point-to-point or broadcast services
- Signal from earth to satellite is called uplink. Uplink signal frequency is 6 GHz
- Signal from satellite to earth is called downlink. Downlink signal frequency is 4 GHz