Solved Assignment Problems – Algorithms and Flowcharts
Algorithm
An algorithm is defined as sequence of steps to solve a problem (task). The steps must be finite, well defined and unambiguous. Writing algorithm requires some thinking. Algorithm can also be defined as a plan to solve a problem and represents its logic. Note that an algorithm is of no use if it does not help us arrive at the desired solution
Algorithm characteristics
- It should have finite number of steps. No one can be expected to execute infinite number of steps.
- The steps must be in order and simple
- Each step should be defined clearly i.e. without un-ambiguity (without doubtfulness)
- Must include all required information
- Should exhibit at least one output
Flowchart
A flowchart is a pictorial (graphical) representation of an algorithm. A flowchart is drawn using different kinds of symbols. A symbol is used for a specific purpose. Each symbol has name.
| Algorithm | Flowchart | Program |
| An algorithm is defined as sequence of steps to solve a problem (task). | A flowchart is pictorial (graphical) representation of an algorithm. | Set of instructions. Instruction is a command to the computer to do some task. |
| Algorithm can also be defined as a plan to solve a problem and represents its logic. | A picture is worth of 1000 words. We can understand more from picture than words. | Implementation of Algorithm or flowchart |
Different algorithms have different performance characteristics to solve the same problem. Some algorithms are fast. Some are slow. Some occupy more memory space. Some occupy less memory space. Some are complex and some algorithms are simple.
Logically algorithm, flowchart and program are the same.
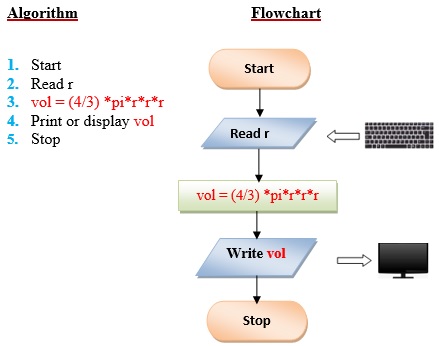
Q1. Create a program to compute the volume of a sphere. Use the formula: V = (4/3) *pi*r3 where pi is equal to 3.1416 approximately. The r is the radius of sphere. Display the result.
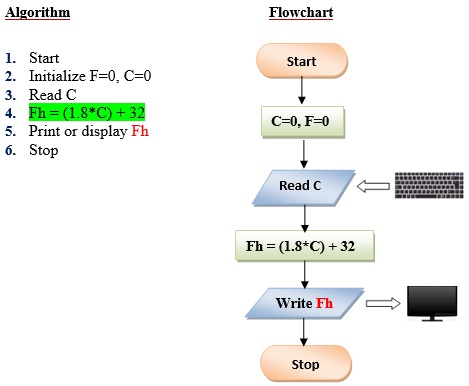
Q2. Write a program the converts the input Celsius degree into its equivalent Fahrenheit degree. Use the formula: F = (9/5) *C+32.
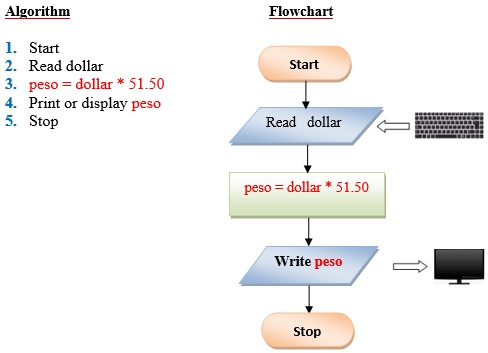
Q3. Write a program that converts the input dollar to its peso exchange rate equivalent. Assume that the present exchange rate is 51.50 pesos against the dollar. Then display the peso equivalent exchange rate.
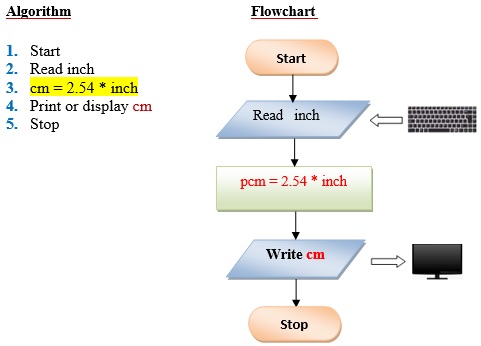
Q4. Write a program that converts an input inch(es) into its equivalent centimeters. Take note that one inch is equivalent to 2.54cms.
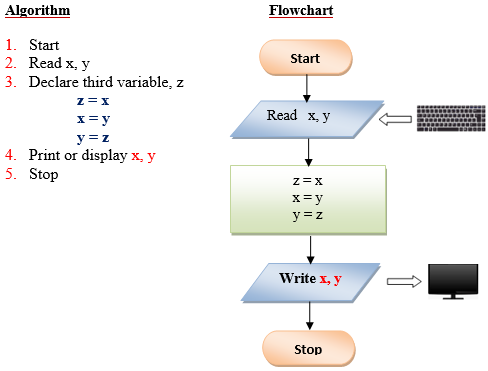
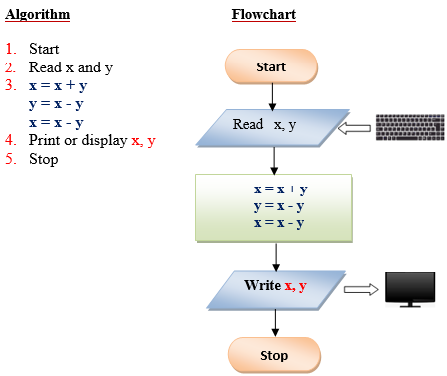
Q5. Write a program that exchanges the value of two variables: x and y. The output must be: the value of variable y will become the value of variable x, and vice versa.
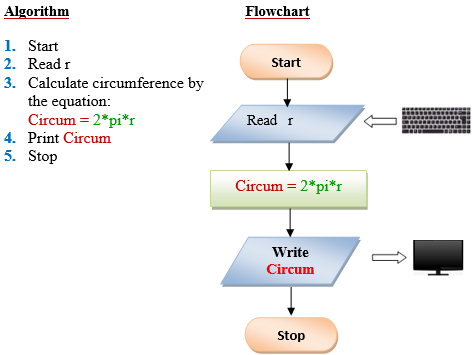
Q6. Design a program to find the circumference of a circle. Use the formula: C=2πr, where π is approximately equivalent 3.1416.
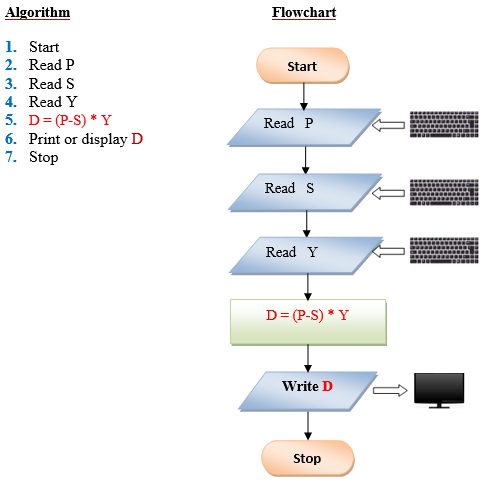
Q7. Write a program that takes as input the purchase price of an item (P), its expected number of years of service (Y) and its expected salvage value (S). Then outputs the yearly depreciation for the item (D). Use the formula: D = (P – S) Y.
Q8. Swapping of 2 variables without using temporary (or 3rd variable).
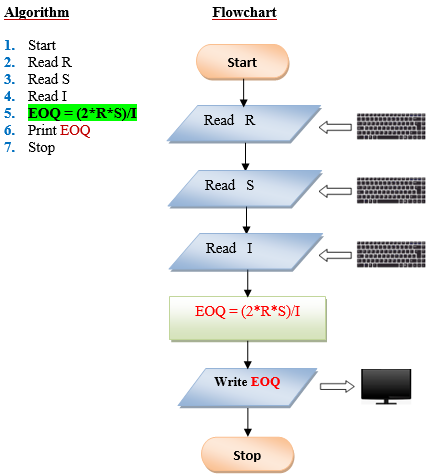
Q9. Determine the most economical quantity to be stocked for each product that a manufacturing company has in its inventory: This quantity, called economic order quantity (EOQ) is calculated as follows: EOQ=2rs/1 where: R= total yearly production requirement S=set up cost per order I=inventory carrying cost per unit.
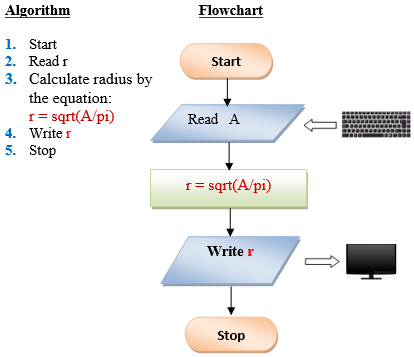
Q10. Write a program to compute the radius of a circle. Derive your formula from the given equation: A=πr², then display the output.