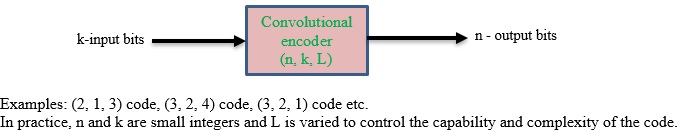
Important terms of convolutional codes
Code rate R
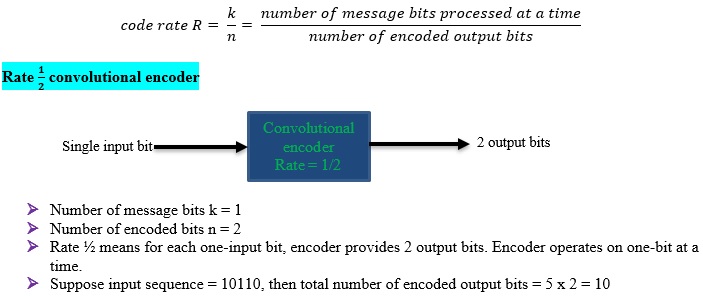
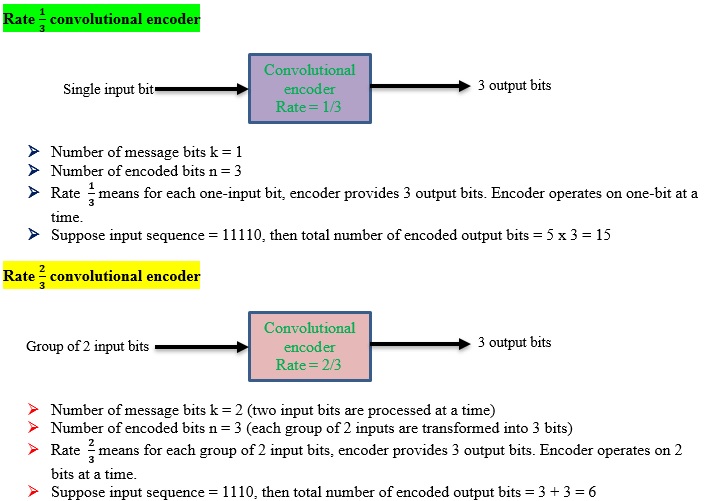
For convolutional codes k and n are usually very small integers
Convolutional codes employed in FEC systems usually have small values of n and k, while constraint lengths typically fall in the range of 10 to 30. All convolutional encoders require a commutator switch at the output.
Constraint length (L)
A convolutional code is described by 3 integers: n, k, L
L = constraint length of encoder. Some authors represent constraint length with letter K
It is defined as the number of shifts over which a single message bit can influence the encoder output bit.
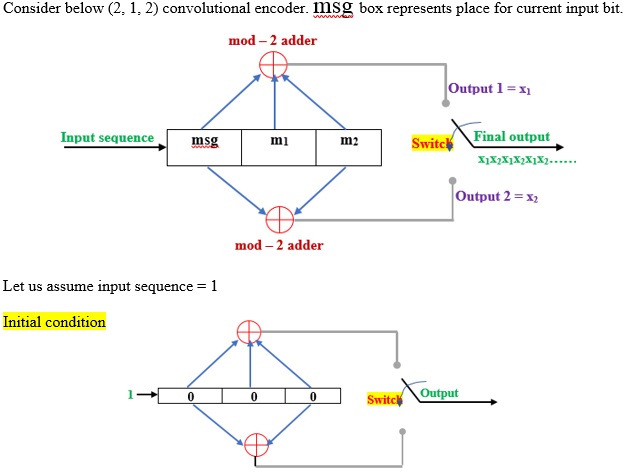
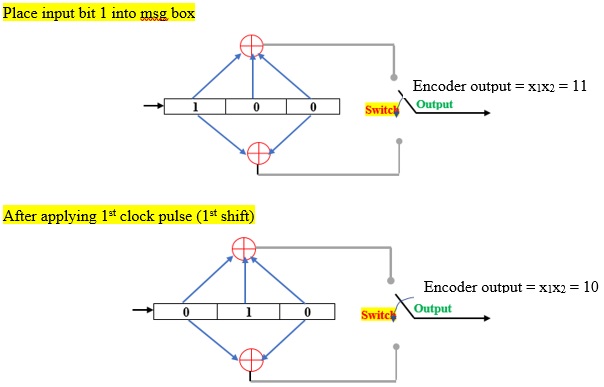
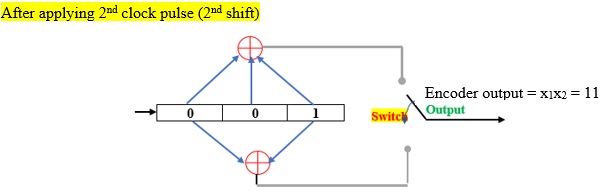
After 3rd clock pulse, the input bit “1” is discarded. So, the input bit 1 influences the output of the encoder for 2 shifts. Hence L (=2) is the number of shifts over which a single message bit can influence the encoder output bit.
Constraint length in terms of encoded output bits:
n(L+1) = 2(2+1) = 2(3) = 6 bits
So, each message bit influences a span of n(L+1) successive output bits. The quantity n(L+1) is called the constraint length measured in terms of encoded output bits. Here L is the encoder’s memory or number of bits used to represent state of the encoder.
L = 3 means single message bit influences encoder output for 3 successive shifts.
Code dimension
A convolutional code is described by 3 integers: n, k, L
L = constraint length of encoder. Some authors represent constraint length with letter K