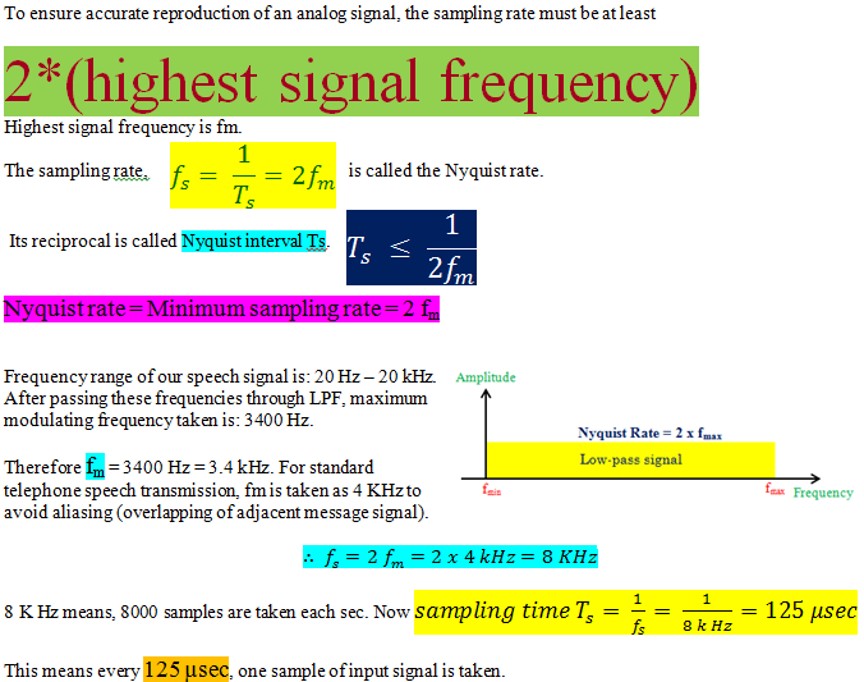
Sampling in PCM | Digital Communications
Sampling
Sampling is the 2nd process in PCM, which is done after band-limiting the message signal.
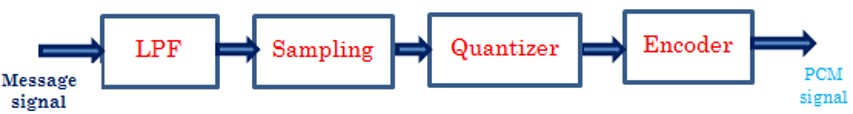
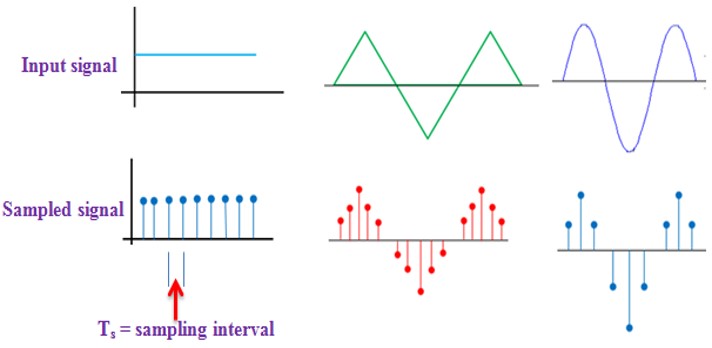
The process by which the continuous-time signal is converted into a discrete–time signal is called Sampling. Sampling operation is performed in accordance with the sampling theorem. The sampling process is illustrated below figures:
Sampling in PCM
- Sampling is also known as Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)
- Sampling process results in signal that is discrete in time but analog in amplitude.
- Examples of discrete values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5…. (value for example 3.7 is an analog value)
- Note that this analog amplitude is converted to discrete value by quantization process
- Sampling is the process of measuring the amplitude of a continuous-time signal at discrete instants.
- It converts a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal.
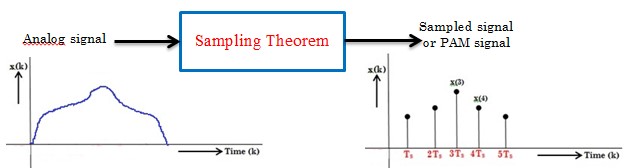

Sampling Theorem
A continuous-time signal may be completely represented in its samples and recovered back if the sampling frequency is . Here fs is the sampling frequency and fm is the maximum frequency present in the message signal.