Types Communication Channels
Types Communication Channels
The Channel provides the electrical connection between the source and destination. It is a physical path between transmitter and receiver.
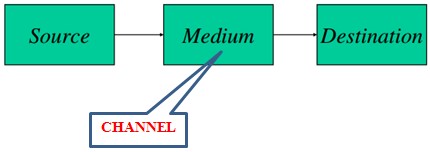
A transmission medium (plural transmission media) is a material (solid, liquid or gas) which can propagate energy waves. For example, the transmission medium for sound received by the ears is air.
The quality of transmission is determined by both the characteristics of the medium and the characteristics of the signal. Transmission medium is a:
- Path between two telephones
- Path between two computers
- Path between the satellite and the ground station in satellite communication systems
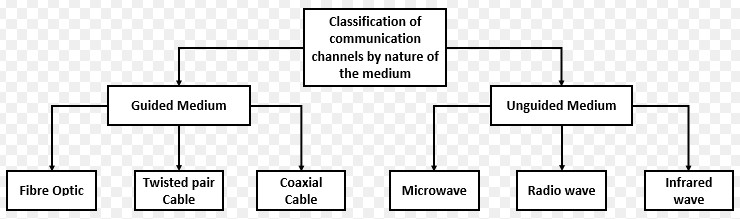
There are two physical ways to transmit data: guided and unguided.
Guided media consists of physical connection between source and destination via a wire or a cable. In guided media, the signals are confined within the wire and guided along a physical path. Examples are twisted pair, coaxial cable and optical fiber.
Unguided media transport electromagnetic (EM) waves without using a physical conductor. This type of communication is often referred to as wireless communication. Examples are atmosphere and outer space (Radio waves, microwaves, infrared) and satellite channels.
Unguided (wireless) transmission is used in geographically disadvantaged places like: desert, forest, hills, mountains, oceans etc., where installing wires, cables is difficult.
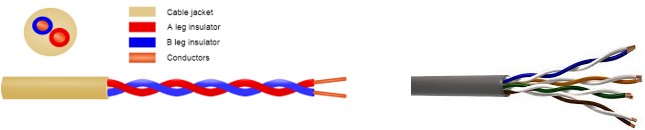
Twisted Pair cable
Wire pairs are commonly used in local telephone communication and for short distance digital data communication. They are usually made up of copper and the pair of wires is twisted together. Data transmission speed is normally 9600 bits per second in a distance of 100 meter.
Commonly used medium and it is quite cheaper than any other transmission media. A twisted pair consists of two insulated conductors twisted together as shown in figure. Twisting is used to decrease interference from other wires.
It can be shielded (cover for extra protection) or unshielded. The unshielded twisted pairs are very cheap and easy to install, but badly affected by noise and interference.
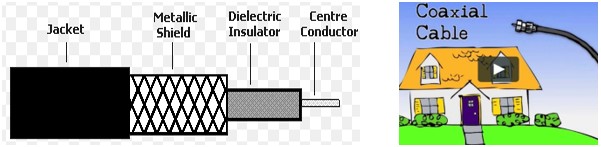
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable consists of a central copper wire surrounded by an insulation over which copper mesh is placed. Coaxial cable is like a pipe with wire suspended in the middle of it. Due to its construction, coaxial cable is less susceptible to interference than twisted pair. Coaxial cable is capable of supporting a much higher frequency range than twisted pair.
One of the most popular use of co-axial cable is in cable TV (CATV) for the distribution of TV programmes. Another importance use of co-axial cable is in LAN and for long distance telephone communication.
Coaxial cable Features
- Two types of cables having 75 ohm and 50 ohm impedance are available
- Because of shielding, this cable has excellent noise immunity
- It has a large bandwidth and low losses
- Most widely used medium for Local Area Network (LANs)
- These cables are costlier than twisted pair cables, but cheaper than optical fibre cables
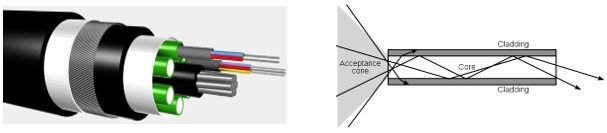
Fibre Optic cable
An optical fiber is constructed from a very thin stand of glass or ultra-pure plastic that is placed in a cladding of glass or plastic. Information is transmitted in the form of light, therefore no electrical interference and supports long distance communication. Note that twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable transport signals in the form of electric signals. Fibre optic operates at optical frequencies (1014 to 1015 Hz). A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads. The main disadvantage of fiber optics is that the cables are expensive to install.
Because of greater bandwidth (2Gbps), smaller diameter, lighter weight, low attenuation, immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and longer repeater spacing, optical fiber cables are finding widespread use in long-distance telecommunications.
- Fibre optic carries information in the form of light
- Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidththan metal cables. This means that they can carry more data.
- Fiber optic cables are less susceptible to interference than other transmission medium.
- Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than wires