Antenna as transmitter and receiver
Antenna as Transmitting Antenna
Here the two-wire transmission line is connected to a RF generator. When a sinusoidal voltage is applied across the transmission line, an electric field is created. As stated in Maxwell’s equations, this electric field creates magnetic field. The spacing between wires is assumed to be a small fraction of a wavelength (λ). the transmission line opens out in a tampered transition. As the separation approaches the order of a wavelength or more, the wave tends to be radiated so that the opened-out line acts like an antenna which launches a free-space wave. The currents on the transmission line flow out on the antenna and end there, but the fields associated with them keep on going. From the circuit point of view the antennas appear to the transmission line as a resistance Rr, called Radiation resistance.
Due to the time varying electric and magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves (EM) are created and these travel between the conductors. As these waves approach open space, free space waves are formed by connecting the open ends of the electric lines. Since the sinusoidal source continuously creates the electric disturbance, electromagnetic waves are created continuously and these travel through the transmission line, through the antenna and are radiated into the free space. Inside the transmission line and the antenna, the electromagnetic waves are sustained due to the charges, but as soon as they enter the free space, they form closed loops and are radiated.
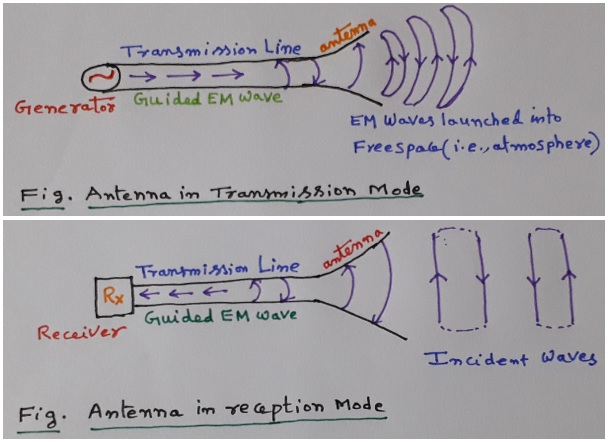
b) Antenna as Receiving Antenna
From the circuit point of view, the antennas appear to the transmission lines as a resistance Rr called the radiation resistance. In the transmitting case, the radiated power is absorbed by objects at a distance: trees, buildings, the ground, the sky, and other antennas. In the receiving case, passive radiation from distant objects or active radiation from other antennas raises the apparent temperature of Radiation by other Antenna or radiation from distant objects raises the apparent temperature of Rr (radiation resistance). Rr may be thought of as virtual resistance that does not exist physically but is a quantity coupling the antenna to distant regions of space via a virtual transmission line.