DPCM | Differential PCM
DPCM (Differential PCM)
DPCM is designed specifically to take advantage of the sample-to-sample redundancies in typical speech waveforms. Note that samples of a signal are highly correlated with each other. Correlation means similarity.
Standard PCM
Standard PCM uses 8 bits to represent each sample.
- Note that 8 bit/sample is the telecommunication industry standard.
- Ideal representation of sample value takes ∞ (infinite) number of bits, which is impossible.
- If number of bits/sample increases, quality of transmission & reception increases
Redundancy
For the signals which do not change rapidly from one sample to next sample, the PCM scheme is not preferred. When such highly correlated (correlation means similarity) samples are encoded the resulting encoded signal contains redundant information. By removing this redundancy before encoding an efficient coded signal can be obtained. One of such scheme is the DPCM technique.
In DPCM, only the difference between current sample and the previous value is encoded as shown in below figure. This can further reduce the number of bits required for transmission.
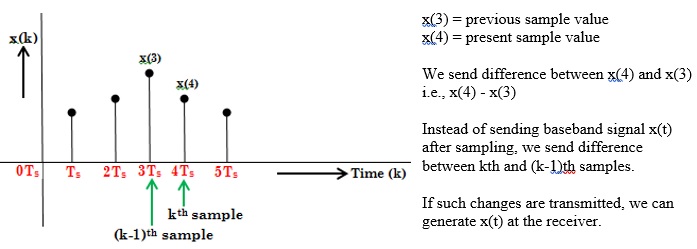
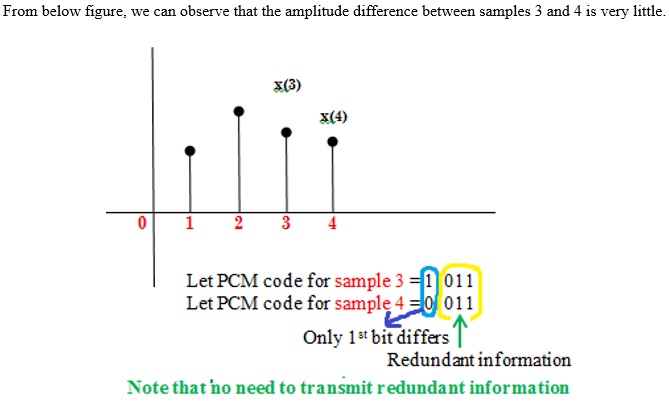

It often happens that the difference between amplitudes of adjacent samples will be very little
DPCM is designed specifically to take advantage of the sample-to-sample redundancies in typical speech waveforms.
Note that samples of a signal are highly correlated with each other. Correlation means similarity.
This is due to the fact that any signal doesn’t change fast i.e., voltage difference from present sample to next sample doesn’t differ by large amount. The adjacent samples of the signal carry the same information with a little difference.
With DPCM, the difference in the amplitudes of two successive samples is transmitted rather than the actual sample value.
PCM systems using differential quantizing schemes are known as DPCM systems. A picture that is quantized to 256 levels (8-bit) may be transmitted using 4-bit differential encoding. This reduces transmission bandwidth by a factor of 2. Transmitted amplitudes are smaller, so requires fewer bits.
From above figure note that no need to transmit redundant information. If this redundancy is reduced then overall bit rate will decrease and number of bits required to transmit one sample will also be reduced. This is DPCM.