Hierarchy of operators in c++
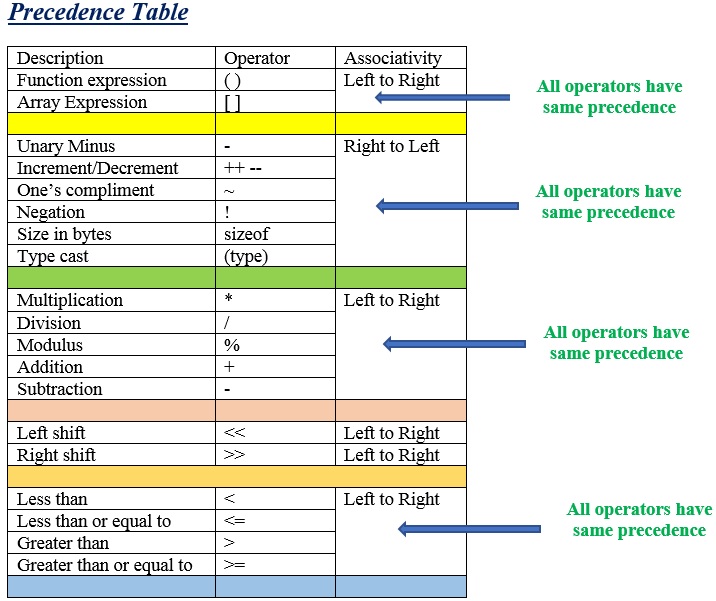
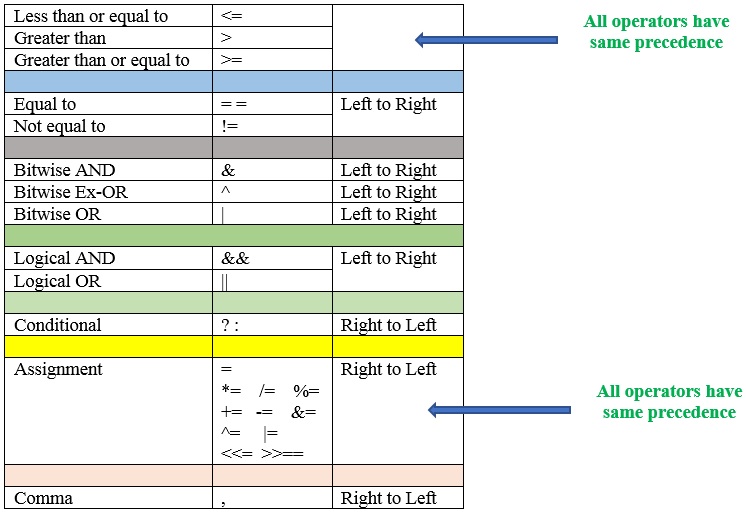
Hierarchy of Operations
While executing an arithmetic statement, which has two or more operators, we mayconfuse to calculate the result. For example, the expression 2 * x – 3 * y correspondsto (2x) – (3y) or to 2(x-3y)? Similarly, A / B * C correspond to A / (B * C) orto (A / B) * C?
To answer these questions, one has to understand the ‘hierarchy’ of operations.The priority in which the operations in an arithmetic statement are performedis called the hierarchy of operations.
Precedence is also known as priority.
Associativity: associativity is the direction in which the compiler evaluates the expression.
Associativity of Operators
When an expression contains two operators of equal priority the tie between them is settled using the associativity of the operators. Associativity can be of two types—Left to Right or Right to Left. Left to Right associativity means that the left operand must be unambiguous. Unambiguous in what sense? Itmust not be involved in evaluation of any other sub-expression. Similarly, incase of Right to Left associativity the right operand must be unambiguous. Let us understand this with an example.
Operators having equal precedence (or priority) are evaluated using associativity.
Consider the expression
a = 3 / 2 * 5;
Here, there is a tie between operators of same priority, that is between / and *.This tie is settled using the associativity of / and *. But both enjoy Left to Right associativity. Figure 1.10 shows for each operator which operand is unambiguous and which is not.
| Operator | Left | Right | Remark |
| / | 3 | 2 or 2*5 | Left operand is unambiguous. Right is not. |
| * | 3/2 or 2 | 5 | Right operand is unambiguous. Left is not. |
Ambiguous means doubt. Unambiguous means clear.
Since both / and * have L to R associativity and only / has unambiguous left operand (necessary condition for L to R associativity) it isperformed earlier.

Note that 6 / 4 gives 1 and not 1.5. This so happens because 6 and 4 both are integers and therefore would evaluate to only an integer constant. Similarly, 5 / 8 evaluates to zero, since 5 and 8 are integer constants and hence must return an integer value.