Functions in C++ Programming
What is a Function
A function is a self-contained block of statements that perform a SPECIFIC TASK. Every C++ program is a collection of functions. Imagine that using a function is like hiring a person to do a specific job. In daily life you may call electrician/car mechanic/plumber to do some job for you. Note that once a function is written you can call it many times in your program by its name. So function is like a worker and specialized in particular work. For example, electrician is specialized in doing electrical work and tailor is specialaized in tailoring.
Why Use Functions
- Using functions is similar to Divide-and-Conquer method. Don’t put entire program logic in a single function. Suppose, when writing a program for calculator, you can write different functions to perform different tasks like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
- Writing functions avoids rewriting the same instructions over and over.
- Enhance the logical clarity of the program
- Helps to avoid repeated programming across program
- Using functions, it becomes easier to write programs and keep track of what they are doing
- Note that each function will perform logically some isolated task
- Adding too many functions and calling them frequently may slow down the program execution
Examples:
int sum(); // here function: sum does not take any arguments
int sum(x, y, z); // here x, y, are arguments to the function, whose name is sum
float subtract(); // here function: subtract does not take any arguments
double divide(); // here function: divide does not take any arguments
int multiply(a, b) // function multiply take two arguments and returns integer value
Function ARGUMENTS are also known as function PARAMETERS. A function may or may not take any arguments.
A simple program to add given two numbers:
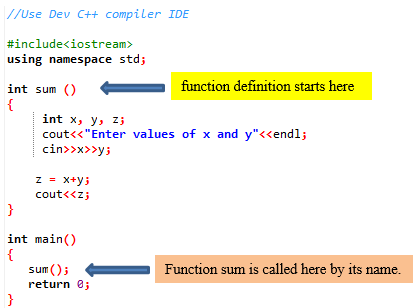
Notes on above program:
- Calling function name: main
- Called function name: sum
- Function sum doesn’t take any arguments here. Remember that a function can take any number of arguments depending on program logic.
- Calling function uses return statement to send results back to called function. Note that return statement can send only one value to calling function. Suppose writing return (a, b) is a mistake. Because return statement can only send one value at a time – return (a) is right.