Simple if – else statement in C++
Simple if – else Syntax
The form of an if statement is as follows:
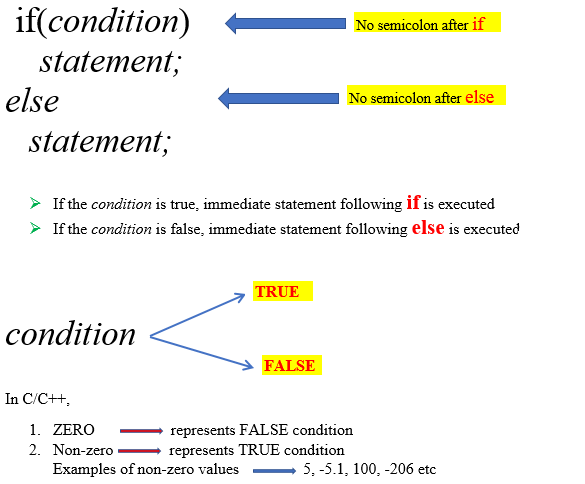

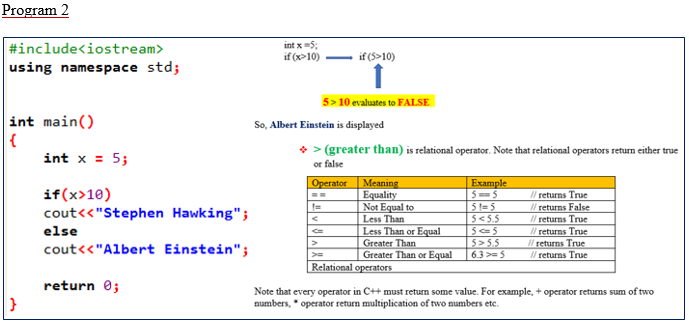
Note that every operator in C++ must return some value. For example, + operator returns sum of two numbers, * operator return multiplication of two numbers etc.
Practice Programs
(i)
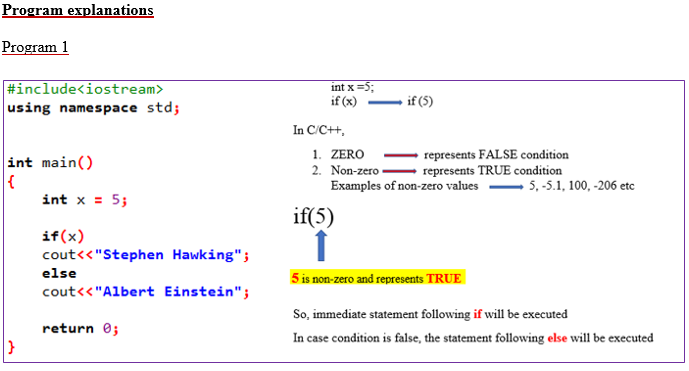
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5;
if(x)
cout<<"Stephen Hawking";
else
cout<<"Albert Einstein";
return 0;
}
(ii)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5;
if(x>10)
cout<<"Stephen Hawking";
else
cout<<"Albert Einstein";
return 0;
}
(iii)
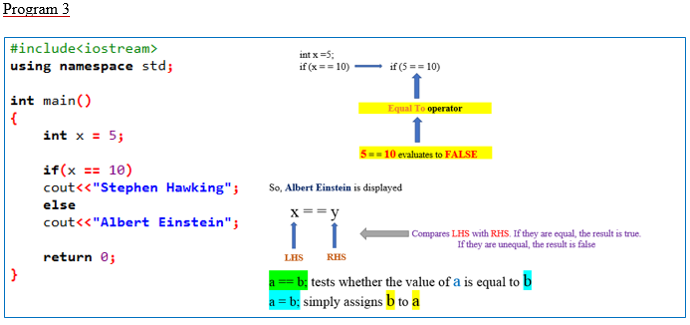
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5;
if(x == 10)
cout<<"Stephen Hawking";
else
cout<<"Albert Einstein";
return 0;
}
(iv)
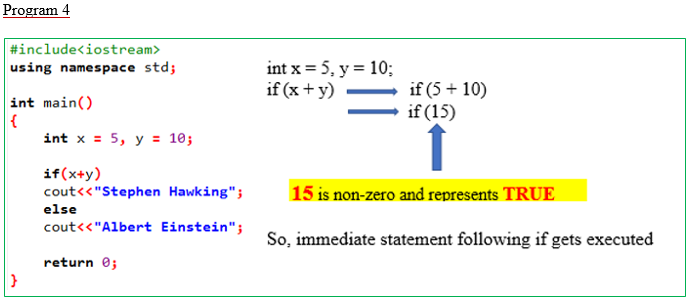
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5, y = 10;
if(x+y)
cout<<"Stephen Hawking";
else
cout<<"Albert Einstein";
return 0;
}
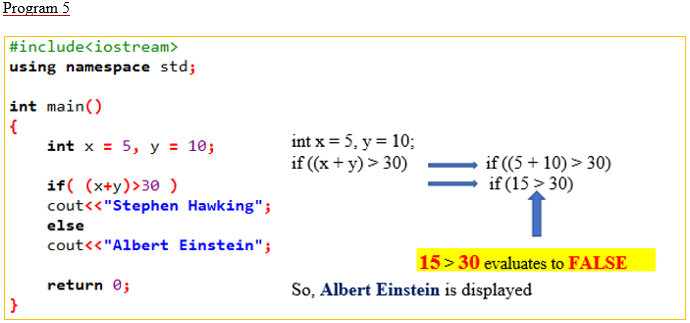
(v)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5, y = 10;
if( (x+y)>30 )
cout<<"Stephen Hawking";
else
cout<<"Albert Einstein";
return 0;
}
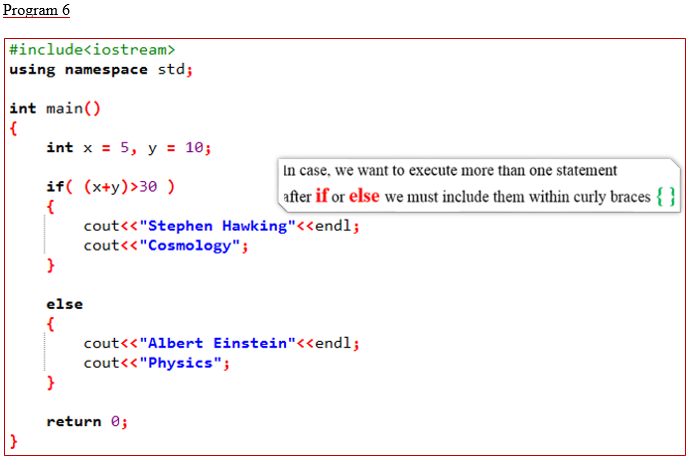
(vi)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5, y = 10;
if( (x+y)>30 )
{
cout<<"Stephen Hawking"<<endl;
cout<<"Cosmology";
}
else
{
cout<<"Albert Einstein"<<endl;
cout<<"Physics";
}
return 0;
}
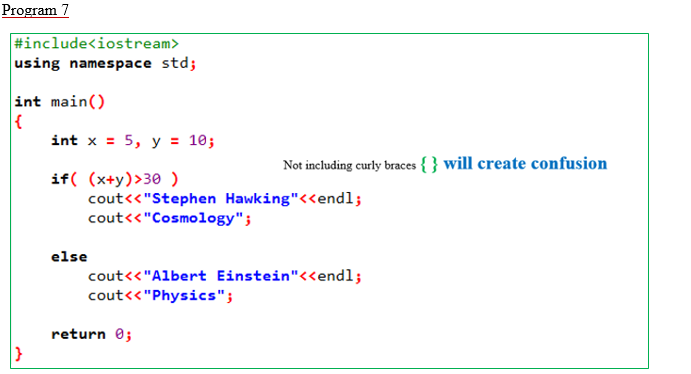
(vii)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5, y = 10;
if( (x+y)>30 )
cout<<"Stephen Hawking"<<endl;
cout<<"Cosmology";
else
cout<<"Albert Einstein"<<endl;
cout<<"Physics";
return 0;
}
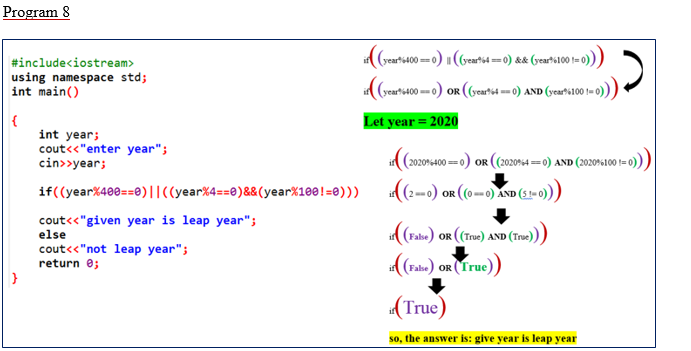
(viii) Testing for Leap year
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int year;
cout<<"enter year";
cin>>year;
if((year%400==0)||((year%4==0)&&(year%100!=0)))
cout<<"given year is leap year";
else
cout<<"not leap year";
return 0;
}