Operators and Expressions in C
Operators
C provides operators for combining arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, and conditional expressions. Note that every operator must return some value. For example, + operator returns sum of two numbers, * operator return multiplication of two numbers etc.
Operator is a symbol that performs some operation. Simple operations may be addition,subtraction, multiplication, divison etc. So, operator is a symbol, which tellsthe compiler to do some operation or action.
For example,
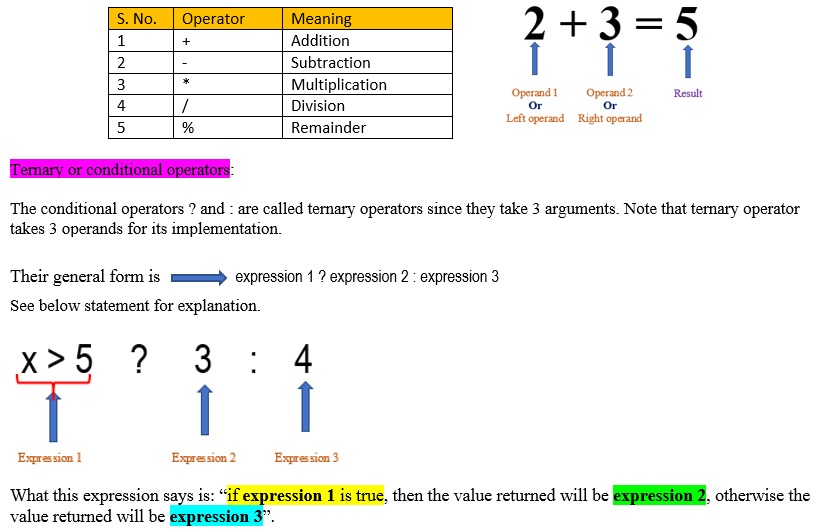
2 + 3 = 5. Here, the data 2 an 3 are known as operands. + is an operator, which perform summation of given numbers 2 and 3. The data 5 is the result of operation.
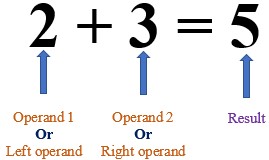
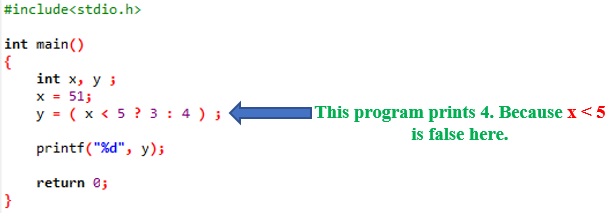
In above expression, the operator + operates on TWO operands. So, + is called binary operator. BI means 2. Rememeber bicycle has two wheels. Binacular has 2 eyes.
5 * 10 =50. Here, the data 5 an 10 are known as operands. * is an operator, which perform multiplication of given numbers 5 and 10. The data 50 is the result ofoperation.
z = x – y. Here, the variables x an y are known as operands. – is an operator, which perform subtracton of given numbers x and y. The result of operation is stored in the variable, z.
List ofsome basic operators is given in below table:
| Operator | Name | Example |
| + | Addition | 12 + 4 // gives 16 |
| – | Subtraction | 3.98 – 2 // gives -1.98 |
| * | Multiplication | 5 * 3.2 // gives 16.0 |
| / | Division | 11 / 2 // gives 5.5 |
| % | Remainder | 10 % 4 //gives 2 |
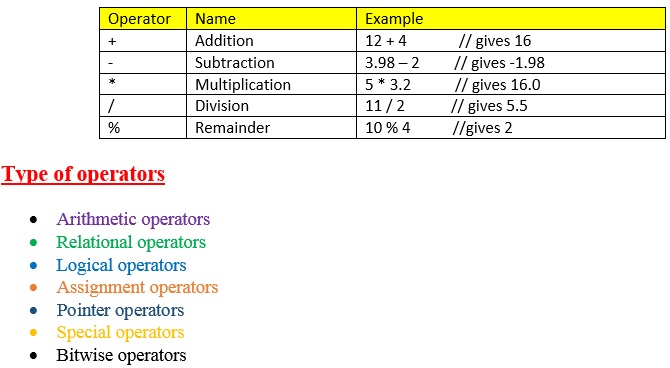
Other classification of operators
- Unary operators
- Binary operators
- Ternary operators
Unary operators:
Some operators operate on single operand. They are called unary operators. Some examples are given below, which will be discussed later.
| S. No. | Symbol | Meaning |
| 1 | ! | Logical Not |
| 2 | ~ | One’s complement |
| 3 | ++ | Increment |
| 4 | — | Decrement |
| 5 | – | Unary minus |
| 6 | * | Pointer operator |
| 7 | & | Address of operator |
| 8 | sizeof | Size of data type |
| 9 | (type) | Type conversion |
Note:
For example, the symbol * can be used for two purposes. It can be used as multiplication operator. And also used as pointer operator. This is known as operator overloading. The process of making an operator to exhibit different behaviours in different instances(times) is known as operator overloading. Real life example of overloading is the use of word: “square”. The word “square” has two meanings. When we saysquare of 5 = 25, the meaning is to find square of a number. Other meaning of asquare is a geometric figure: SQUARE.
Binary operators:
Some operators operate on two operands. They are called binary operators. Some examples are given below, which will be discussed later.