What is modulation and demodulation
Modulation
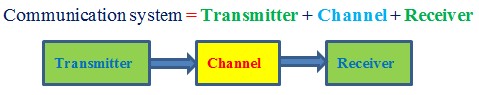
Modulation is an activity or process that takes place in TRANSMITTER section of a communication system.
Modulation is the fundamental requirement of any communication system.
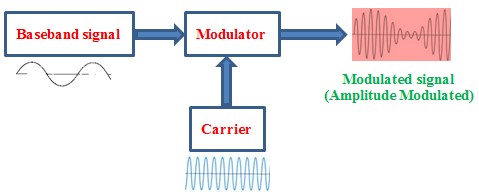
The two signals involved in modulation process are: baseband signal and carrier.
- Modulating signal = baseband signal
= information bearing signal
= message signal
= input signal
= intelligence signal
- Modulating or baseband signal is LF
- Baseband or message signals are generated by information sources like microphone, camera, type writer etc.
- Real-life examples of baseband signal: voice, audio, music, video, computer data
- Carrier signal
- Carrier: as the name suggests, its job is to carry the signal from one place to other.
- Carrier is a HF signal
- Sine or cosine wave are used as carrier in analog modulation techniques such as AM, FM
- Real-life examples of carrier signal: Bus, Train, Airplane etc.

Modulation definition:
Modulation is the process by which some characteristic (amplitude, frequency, or phase) of the carrier is changed according to amplitude of the input (baseband signal). In case of voice signal, the value of amplitude depends on the LOUDENESS. The more loudly we speak, more the amplitude value.
- In Amplitude Modulation (AM), amplitude of the carrier is changed in accordance with amplitude of modulating signal.
- In Frequency Modulation (FM), frequency of the carrier is changed in accordance with amplitude of modulating signal.
- In Phase Modulation (PM), phase of the carrier is changed in accordance with amplitude of modulating signal.
- Transmitter modifies the message signal in order to transport information easily from one place to other. This modification is called modulation.
- During this process, Low Frequency (LF) signal changes the High Frequency (HF) signal.
- By modulation, baseband signal is translated from Low Frequency (LF) to High Frequency (HF).
Why Modulation?
- Easy transportation of baseband signals
- Long distance communications
- Put a stone around paper and through it. Observe the distances travelled with and without stone. Here stone is a carrier and paper is modulating signal. Note that carrier (stone) does not contain any information. Paper only contains information.
- Modulation allows smaller size of antenna.
- The effect of modulation is to increase the frequency of input signal so that antenna size is reasonably small and practically achievable.
- For successful transmission and reception of baseband signals
- To allow use of multiplexing
- To reduce interference and noise
- Carrier frequency fc must be greater than modulating frequency fm. That means modulating signal is at LF and carrier must be HF sinusoidal (sine wave or cosine wave) signal. Signal resulted from modulation process is called modulated wave.
Dodulation
Process of removing carrier from modulated wave is known as demodulation or detection.