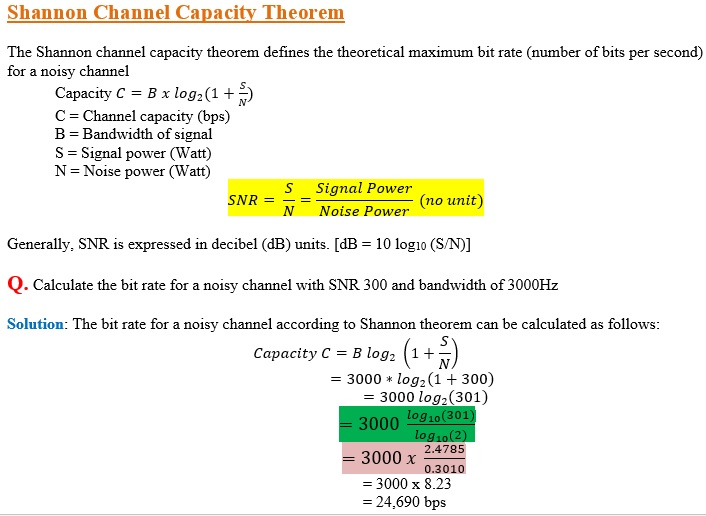
Signal Bandwidth vs Channel Bandwidth
BANDWIDTH
- Bandwidth is the difference between upper and lower frequency limits of the signal
- It is defined as the range of frequencies that the signal occupies.
- Bandwidth can be defined as the portion of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum occupied by the signal.
- It may also be defined as the frequency range over which a signal is transmitted.
- It is one way of describing the maximum amount of information that the channel can carry.
- Frequency range of the signal is known as bandwidth
Note that greater the bandwidth of a channel, higher the data rate. Ideally channel should provide more bandwidth and signal must occupy less bandwidth.
Different types of signals have different bandwidth. Ex. Voice signal, music signal, etc
| Type of the signal | Frequency range (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) |
| Voice (speech) | 300-3400 | 3100 |
| Music signal | 20-15000 | 14,980 |
| TV (picture) signal | 0-5Mega | 5 MHz |
| Digital data | 300-3400 (using telephone line) | 3100 |
BANDWIDTH OF A SIGNAL
Bandwidth of analog and digital signals is calculated in separate ways. In analog technology, the bandwidth is the difference between the lowest and highest frequencies that can pass through the channel. Analog signal bandwidth is measured in terms of its frequency (Hz) but digital signal bandwidth is measured in terms of bit rate (bits per second, bps). Also note that bandwidth of signal is different from bandwidth of the channel.
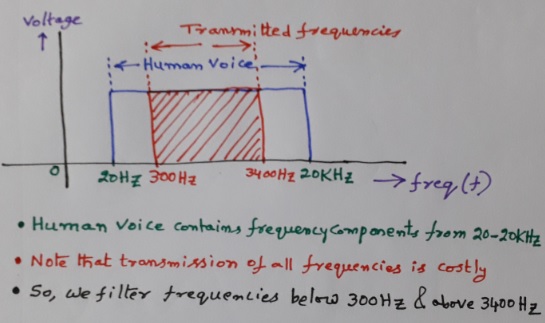
The range of human voice (speech) is 20 Hz – 20 kHz. This is the total voice bandwidth. But the voice frequencies from 300 Hz – 3400 Hz are only transmitted in communications. Note that transmission of all frequencies (20-20kHz) is costly. For efficient transmission and reception of speech signal, 300 – 3400 Hz is sufficient. So, effective speech bandwidth is 3400 Hz – 300 Hz = 3100 Hz.
BANDWIDTH OF A CHANNEL
A channel is the medium through which the input signal passes. In terms of analog signal, bandwidth of the channel is the range of frequencies that the channel can carry. In terms of digital signal, bandwidth of the channel is the maximum bit rate supported by the channel. i.e. number of bits per second that the channel can carry.
The bandwidth of the medium should always be greater than the bandwidth of the signal to be transmitted else loss of information takes place.
Different types of channels have different bandwidth. Ex. Twisted pair, coaxial cable, fibre optics etc.
| Type of the channel | Frequency range (Approx.) |
| Twisted pair | 1MHz – 100 MHz) |
| Coaxial cable | 0 – 750 MHz |
| Microwave | 1 GHz-30 GHz |
| Satellite | 1 GHz – 40 GHz |
| Fibre optics | 180 THz – 330 THz |