Frequency, Wavelength and Phase of a signal
Frequency (f)
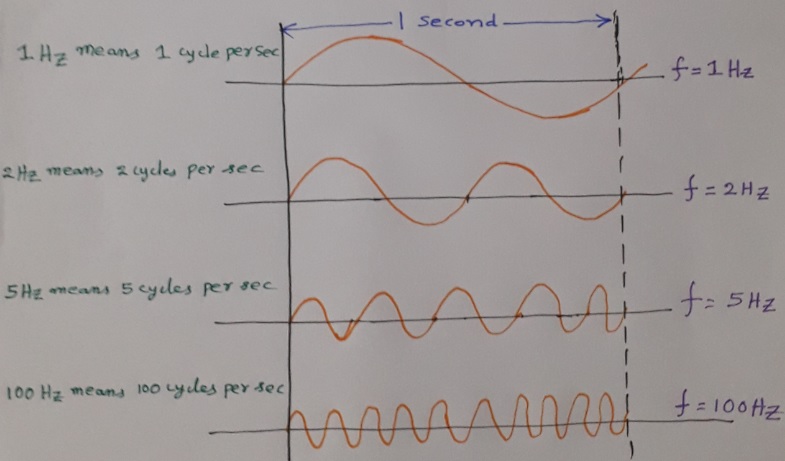
Frequency is defined as the number of cycles completed by the wave in one second i.e., number of cycles per second. Time period refers to the time taken by the wave to complete one second. Unit of frequency is Hz (Hertz). Note that kHz, MHz, GHz, THz are used to measure higher frequencies.
1KHz = 1 Kilo Hertz = 103 Hz 1MHz = 1 Mega Hertz = 106 Hz 1GHz = 1 Giga Hertz = 109 Hz 1THz = 1 Tera Hertz = 1012 Hz
Wavelength (l)
Definition 1: Distance between two identical points on successive cycles of a wave
Definition 2: Distance occupied by the electromagnetic wave (i.e., radio wave) during the one cycle time
Wavelength is usually expressed in meters. Note that very high frequency wavelengths are sometimes expressed in centimetres (cm).
As EM (Electro-Magnetic) waves travel at the speed of light in the free space (atmosphere), their wavelength is given by:

Note that for an EM wave, wavelength = distance occupied by the signal during one cycle time in free-space. Therefore, the answer is 2 metres.
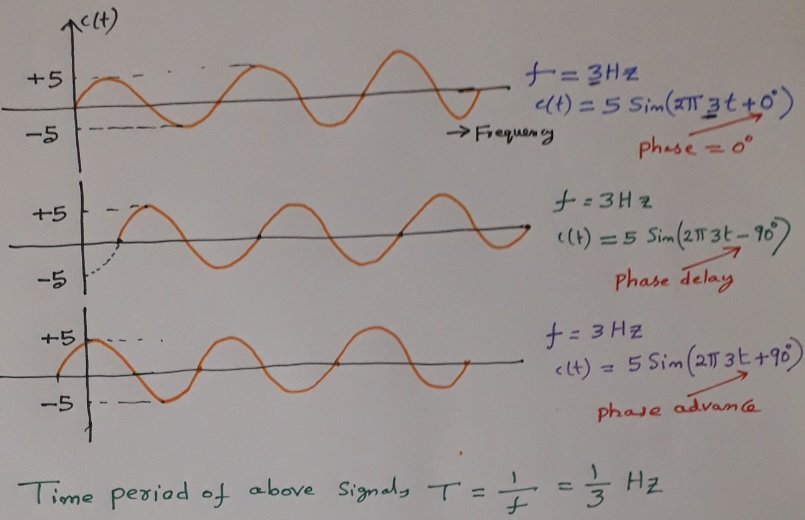
A simple sine wave and its parameters
The sine wave is the simplest form of an analog signal. It has three parameters: amplitude, frequency and phase. Phase describes the position of the waveform with respect to time (specifically relative to time 0). Below figure shows various phase differences (0o, 90o delay or advance) of same sine signal.