Introduction to Antenna communications
Introduction
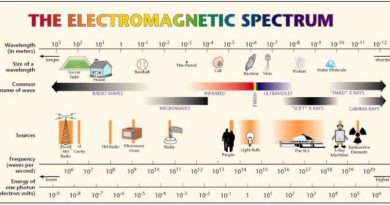
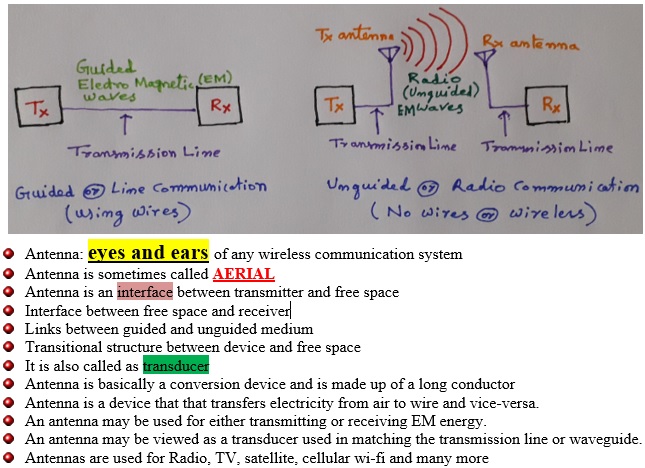
Antenna is a vital (important) component of any wireless communication system. Also we cannot think of wireless communication without antenna. Understanding background concept will help in designing new versatile antennas. An antenna is a metallic conductor system capable of radiating and collecting EM energy. EM wave is the oscillation of electromagnetic (EM) field. An antenna is a device to transmit and/or receive electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves are often referred to as radio waves. An antenna must be tuned (matched) to the same frequency band as the radio system to which it is connected, otherwise reception and/or transmission will be impaired.
Transmitting antenna
Antenna converts electrical energy into EM waves and EM waves are emitted into space. So these antennas are used to radiate RF (Radio Frequency) energy into free space. A transmitting antenna takes a voltage from the transmitter and converts it to an EM (electromagnetic) signal. Ideally transmitting antenna radiates maximum energy into surroundings.
Receiving antenna
Antenna converts EM waves collected from free space into electrical energy. So these are designed to capture RF energy from free space. A receiving antenna has a voltage induced into it by the EM signal that passes across it. The voltage is then connected to the receiver. Note that no risk of electric shock with EM signal, but some radiation is dangerous to health. Ideally receiving antenna collects maximum energy from surroundings. Note that in both cases, the properties of the antenna – gain, directivity, frequency of operation etc are the same.
Diplexer
In many radio communication systems, the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving. In this case, the energy must be computed from heavy-duty materials. A special coupling device called DIPLEXER can be used to direct the transmit and receive signals and provide the necessary isolation. An antenna can transmit and receive at the same time only if a device such as a DIPLEXER is used to keep the transmitter energy out of the receiver.
An antenna can transmit and receive at the same time as long as some means is provided for keeping the transmitter energy out of the front end of the receiver. A device called DIPLEXER is used for this purpose.
An antenna used for transmitting high power (ex. Radio/TV, broadcast stations) must be constructed of materials that can withstand the high voltages and currents involved. A receiving antenna, no matter what the design, can be made of wire. But a transmitting antenna for high power applications might e.g., be designed in the same way but be made of larger, heavier material such as metal tubing.